
If You Are Seeing This Message That Means Javascript Has Been Disabled On Your Browser Please Enable Js To Make This App Work Please Enter A Question First Close Button Camera Button Send Button Loading Getting Image Please Wait Play The
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreAnd therefore the equation is exact Now we must find a function F ( x, y) satisfying (1) and (2) Let's try the indefinite integral (or antiderivative, if you prefer) F ( x, y) = ∫ ∂ F ∂ x d x = x e 2 y − sin x y g ( y), where g ( y) plays the role of constant of integration
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0
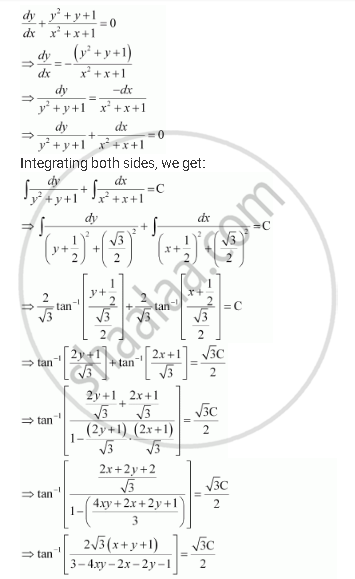
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0-Questions from Continuity and Differentiability 1 If x = s i n − 1 ( 3 t − 4 t 3) and y = c o s − 1 ( 1 − t 2), then d y d x is equal to 2 The derivative of sin − 1 ( 2 x 1 − x 2) with respect to sin − 1 ( 3 x − 4 x 3) is 3 If x = 1 − t 1 t;Let's multiply both sides times 1 plus 2y squared We get 1 plus 2y squared times dy dx is equal to y cosine of x We still haven't fully separated the y's and the x's Let's divide both sides of this by y, and then let's see We get 1 over y plus 2y squared divided by
Differentiation Gradient Problems Ppt Download
\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dxEasy as pi (e) Unlock StepbyStep Natural Language Math Input Take x x = X l;
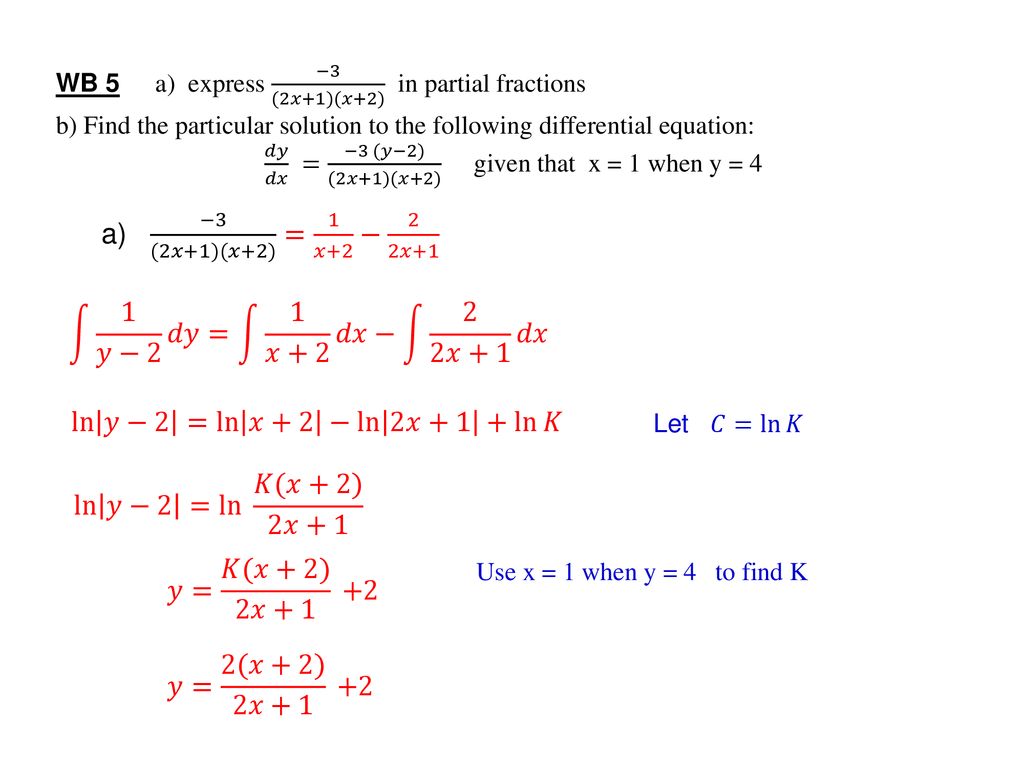
Get stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!0 16k views Solve ( x 2 y − 2 x y 2) d x − ( x 3 − 3 x 2 y) d y = 0 written 39 years ago by smitapn612 ♦ 100 modified months ago by sanketshingote ♦ 740 engineering mathematics 2 ADD COMMENT EDIT 1 AnswerY = Y m (∵ ∵ l and m are constants) So, dy dx d y d x = dY dX d Y d X Therefore, the equations becomes (in X, Y) dY dX d Y d X = X2Y ℓ2m−3 2XY 2ℓm−3 X 2 Y ℓ 2 m − 3 2 X Y 2 ℓ m − 3 = X2Y 2Xy X 2 Y 2 X y If l, m are chosen to satisfy ℓ ℓ 2m 3 = 0 2ℓ ℓ m 3 = 0
X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 | ||
 | 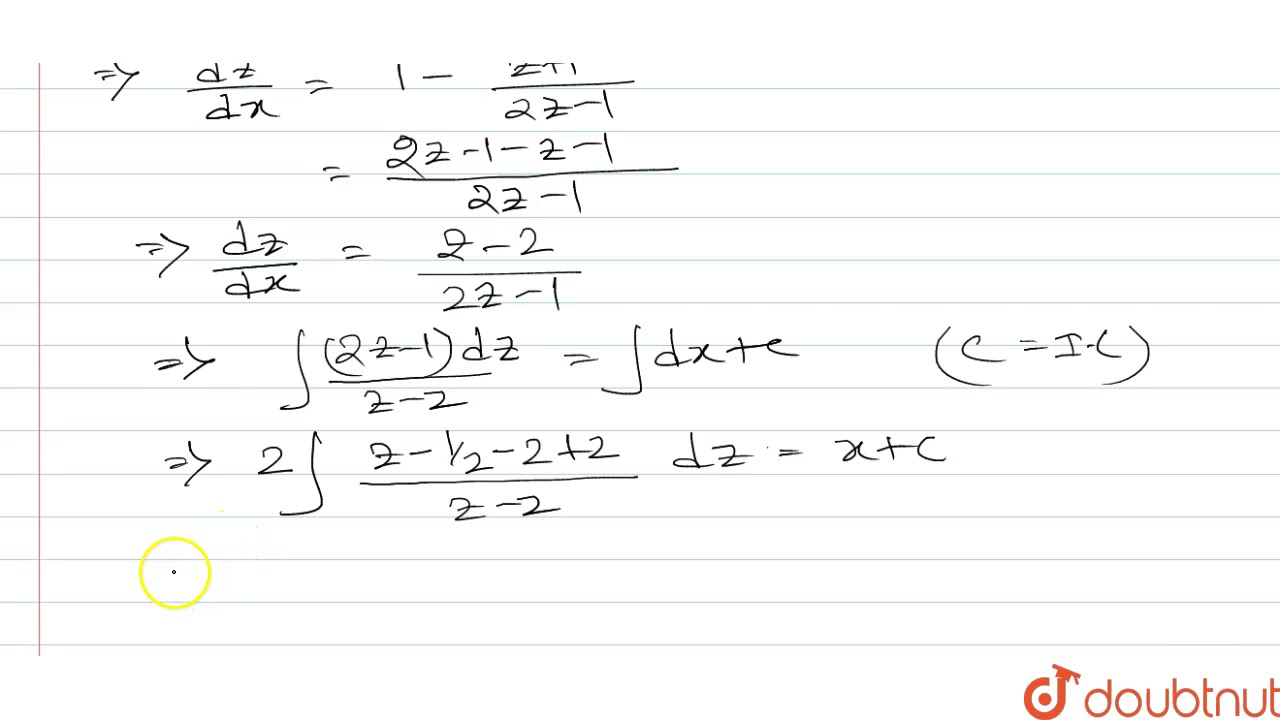 | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | 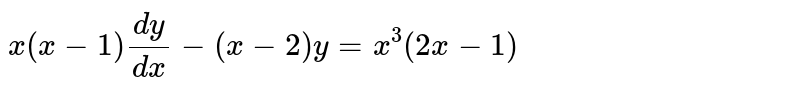 |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 | 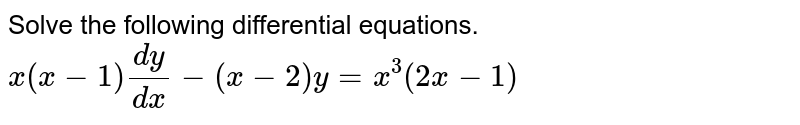 |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
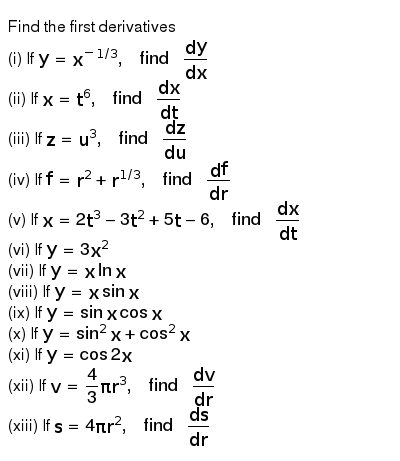 |  | |
 | ||
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
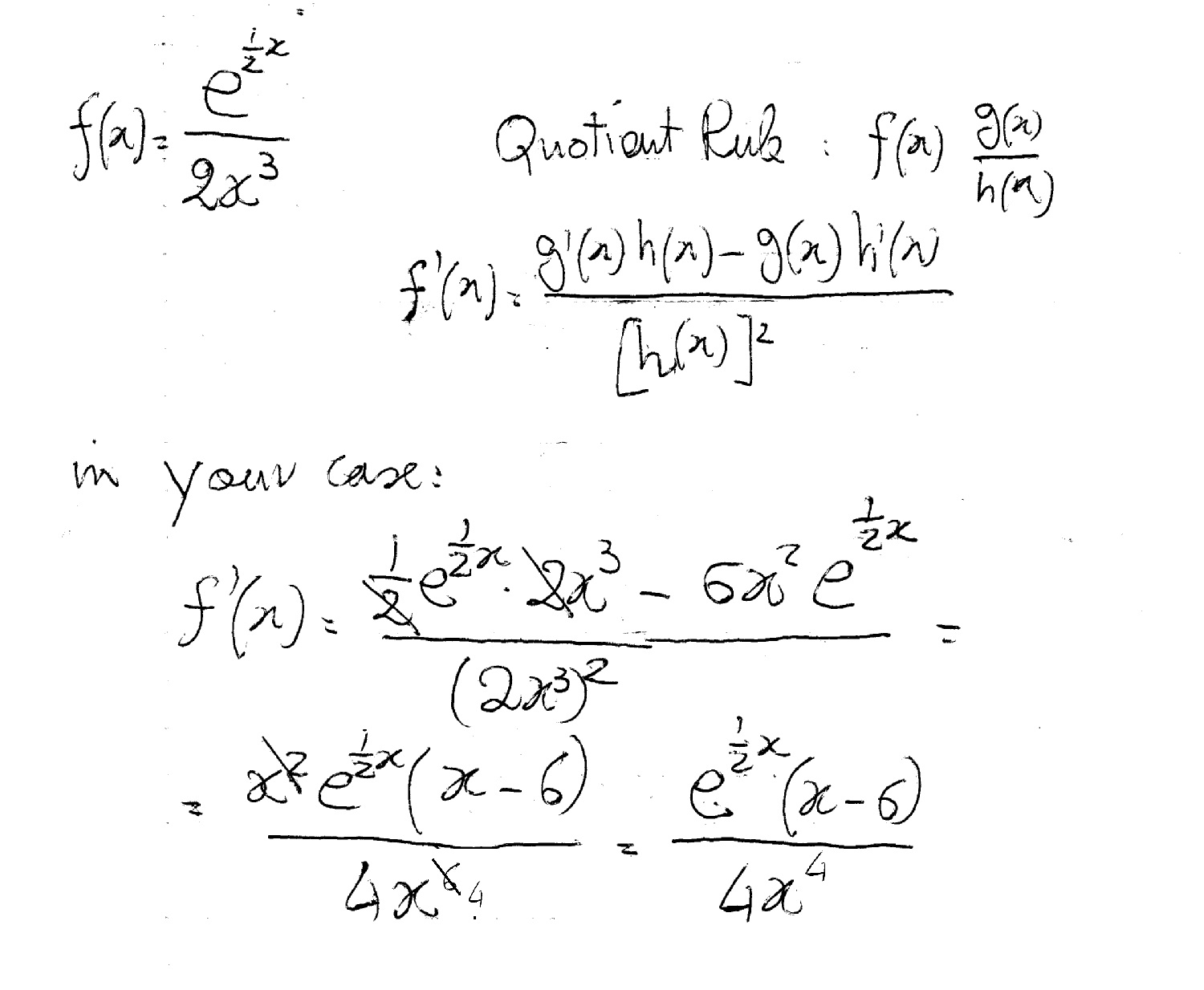 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
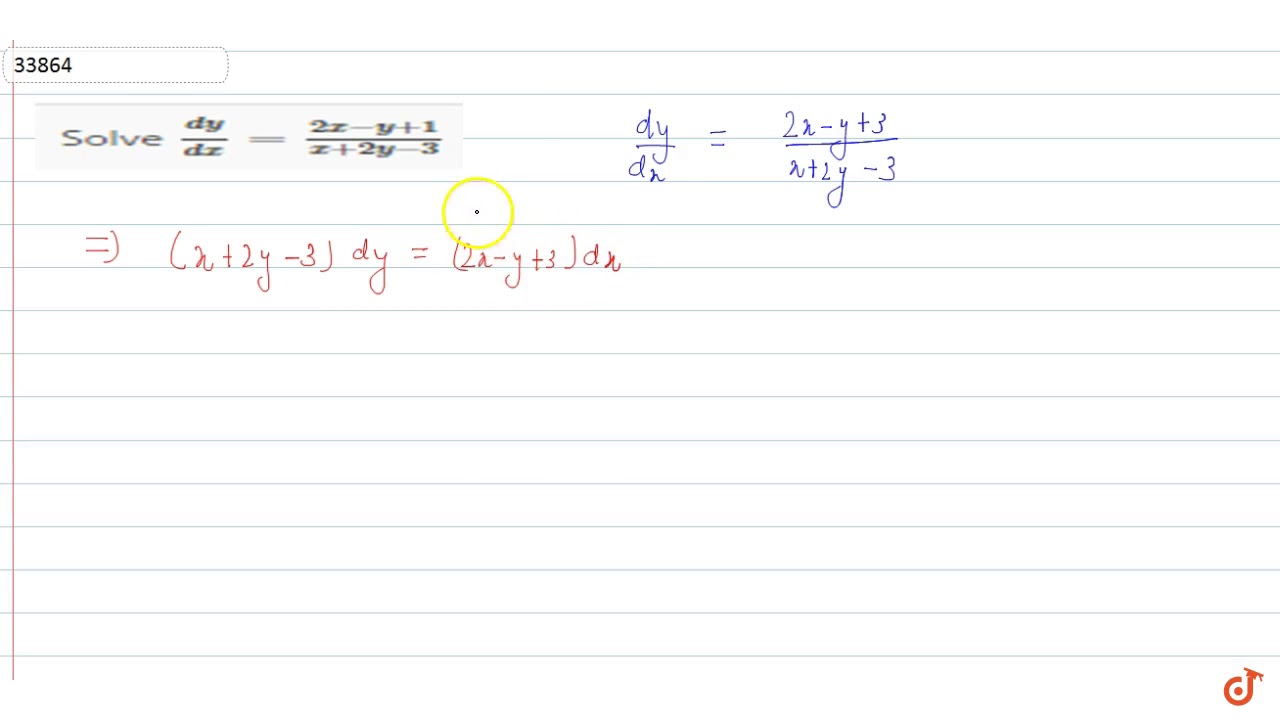 |  | |
 |  |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | ||
 | 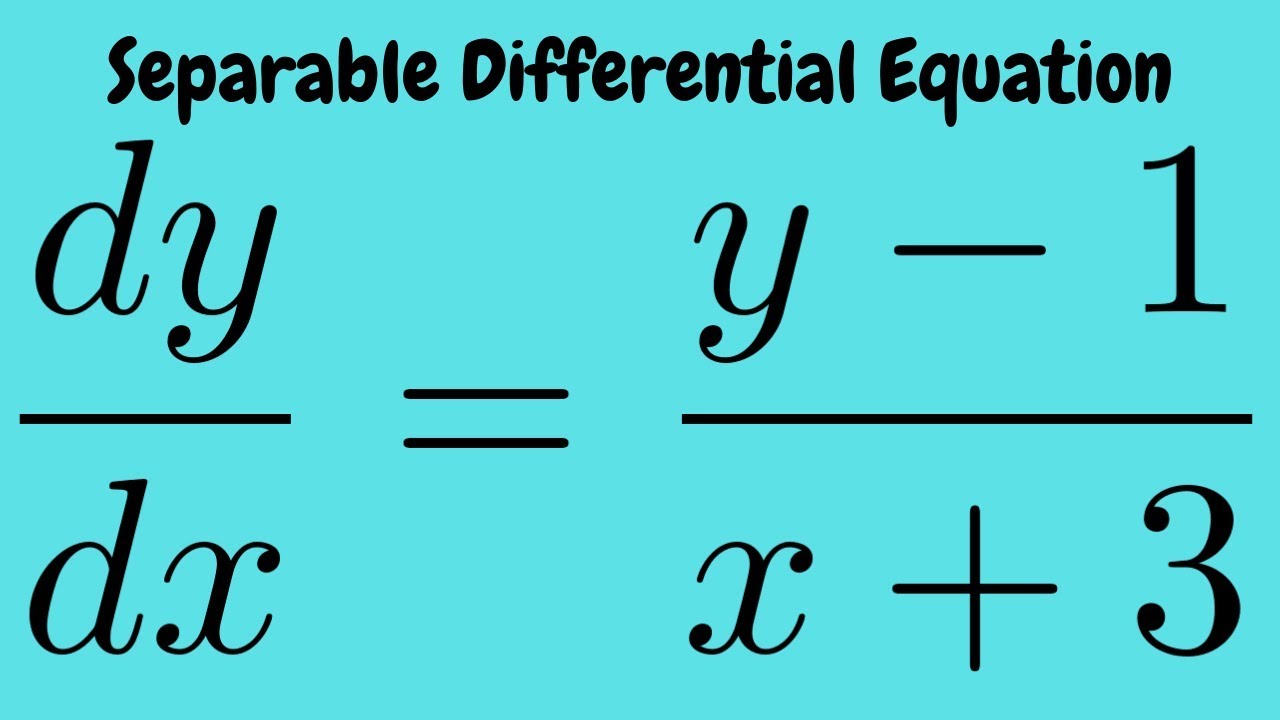 |  |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 | 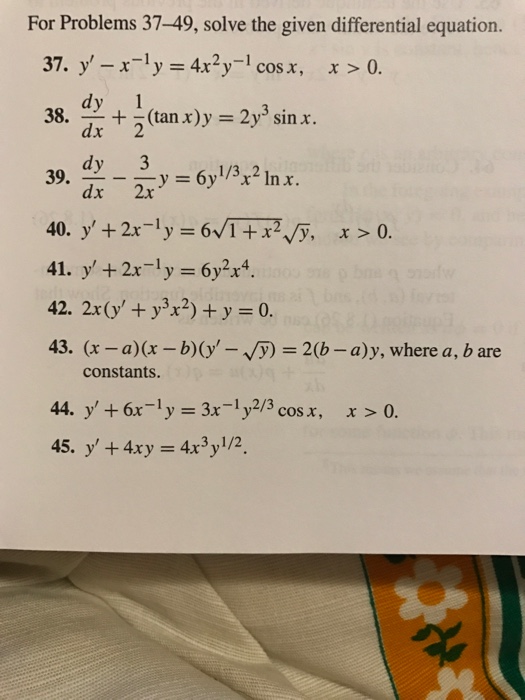 |  |
 |  | |
「X 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 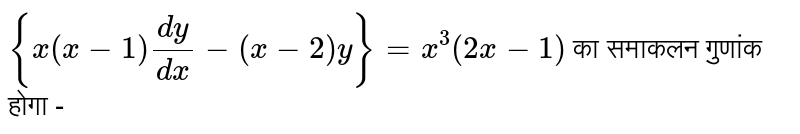 | |
 |
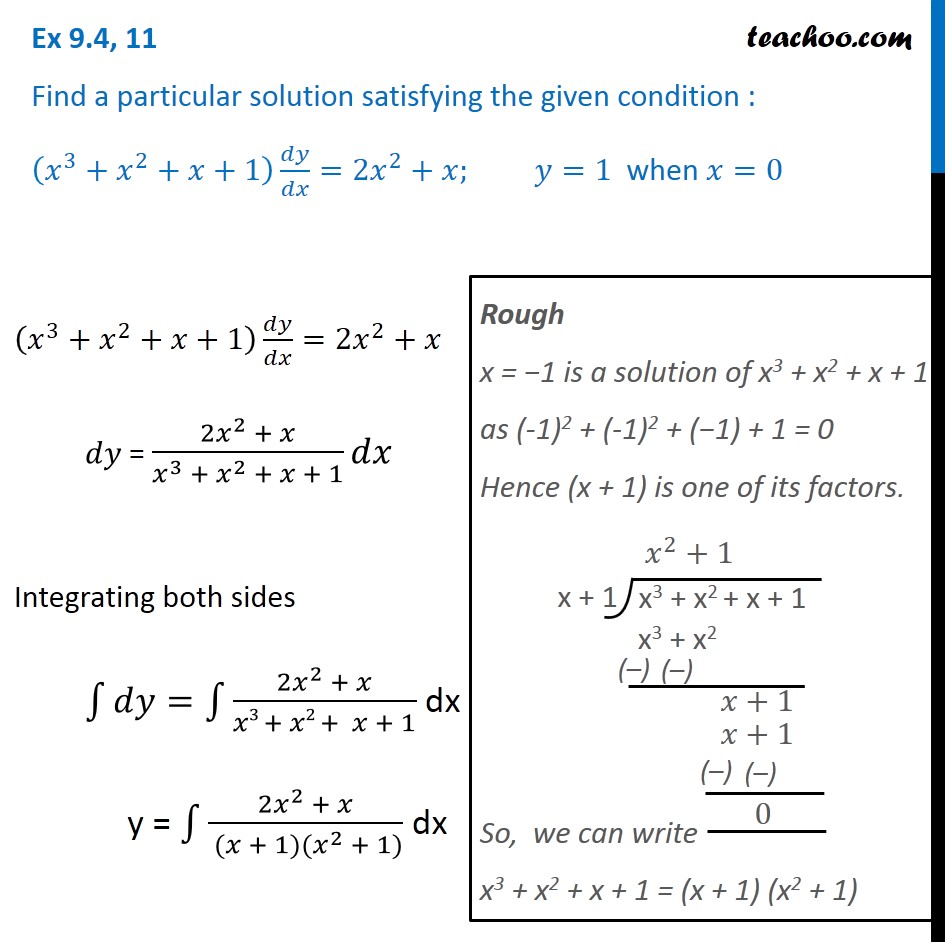
Most Used Actions \mathrm {implicit\derivative} \mathrm {tangent} \mathrm {volume} \mathrm {laplace} \mathrm {fourier} See All area asymptotes critical points derivative domain eigenvalues eigenvectors expand extreme points factor implicit derivative inflection points intercepts inverse laplace inverse laplace partial fractions range slope𝑦=1 when 𝑥=0 (𝑥^3𝑥^2𝑥1) 𝑑𝑦/𝑑𝑥=2𝑥^2𝑥 𝑑𝑦 = (2𝑥^2 𝑥)/(𝑥^3 𝑥^2 𝑥 1) 𝑑𝑥 Integrating both sides ∫1 〖𝑑𝑦=∫1 (2𝑥^2 𝑥)/(𝑥3 𝑥2 𝑥 1)〗 dx y = ∫1 (2𝑥^2 𝑥)/( (𝑥
Incoming Term: x 3 x 2 x 1 dy / dx 2x 2 x y 1 when x 0,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿